Artistry in the Making #2 - Update!
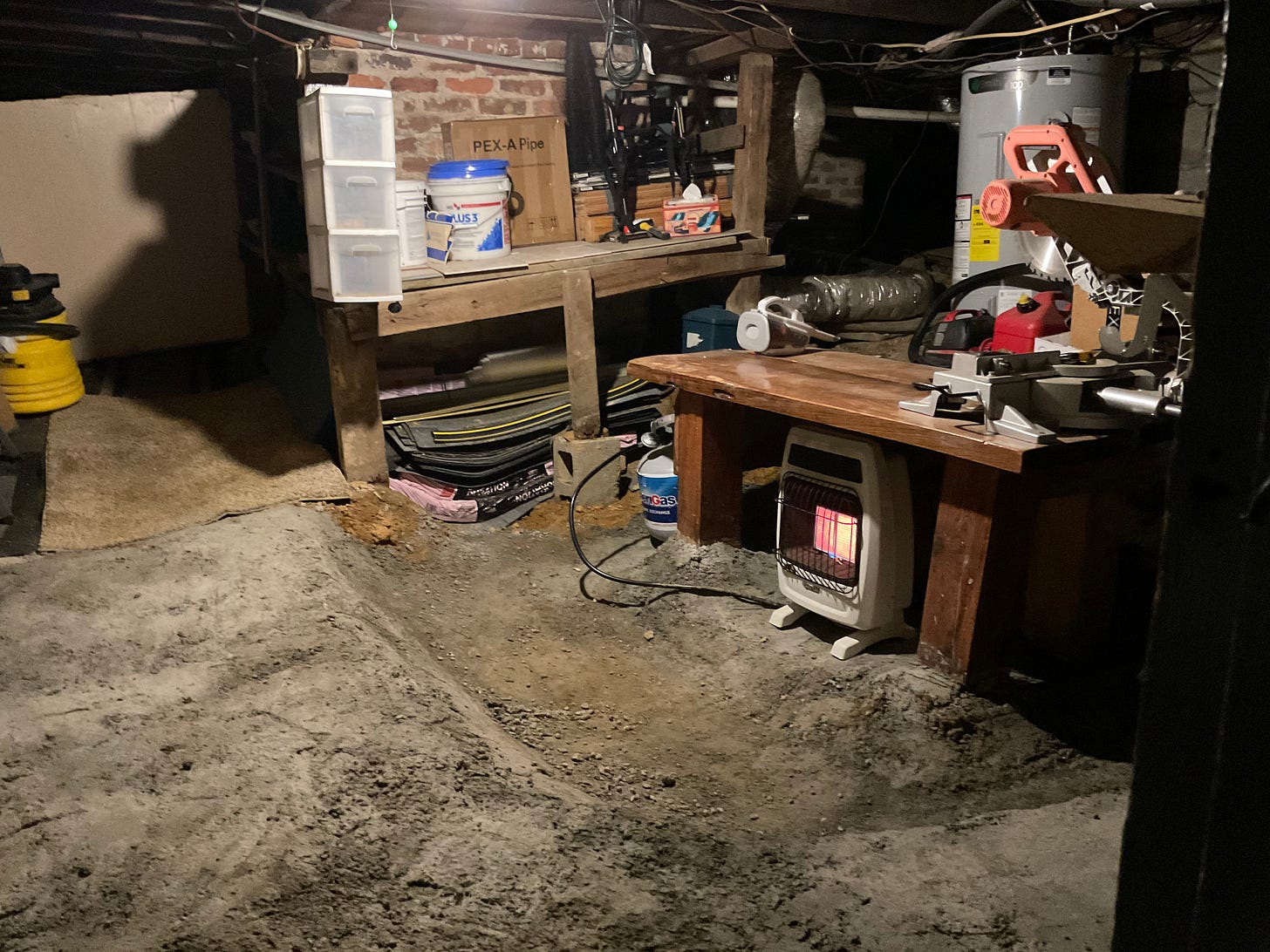
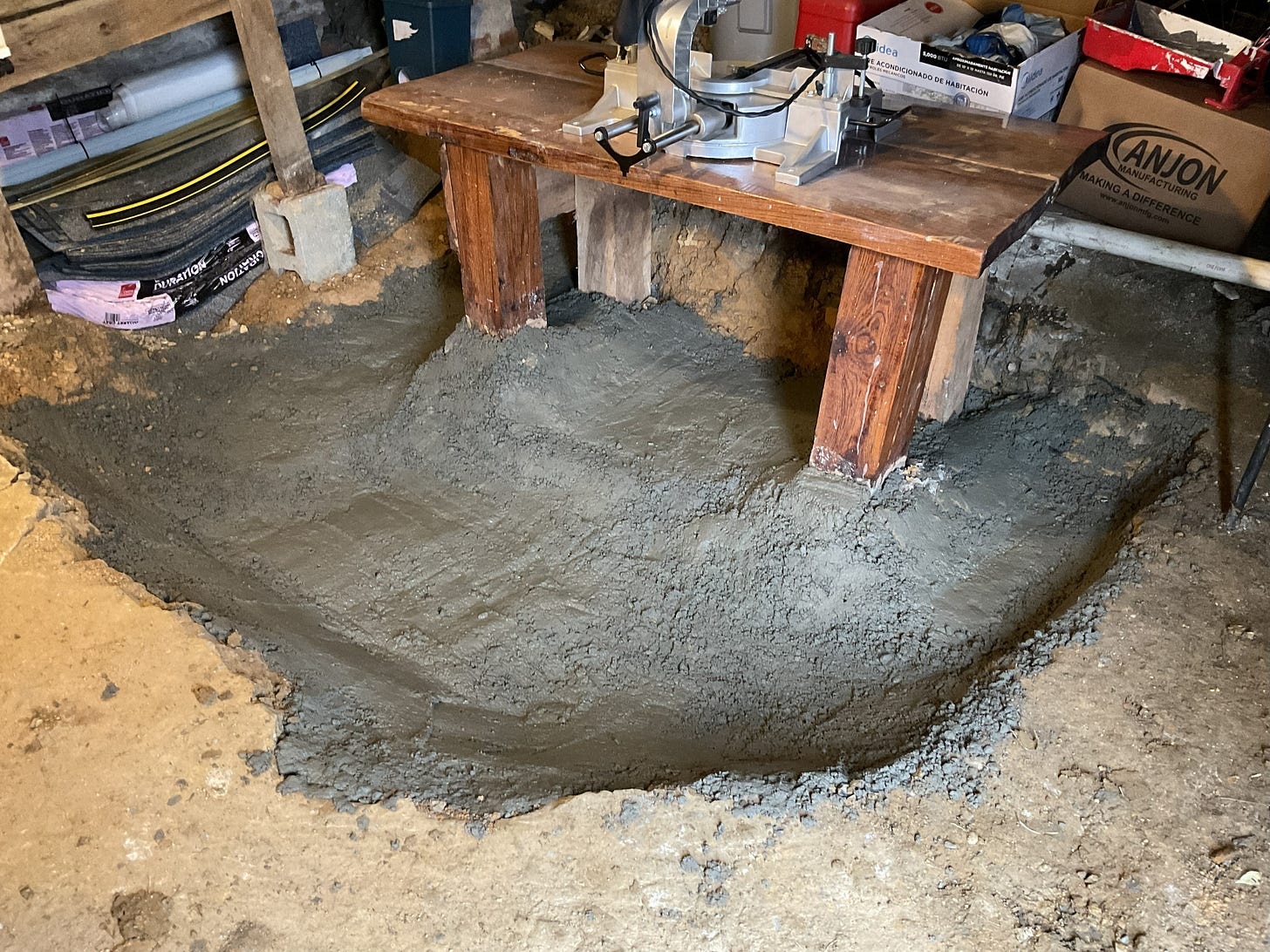
With the addition of some "rough concrete" as well as general tidying up - the Workbench is now in a Workshop - Up and Coming I Hope!
I think I’ve tried to share here at Substack that I have a “lot going on” at our “Getaway Place” and lets be honest without a good workbench in a workshop how is one going to get work done efficiently? I enjoy getting things of merit accomplished and learning from the experience. I don’t mind physical labor - in fact I’d say I enjoy it.
So - here is an update on this “Artistry” article that has taken on a life of its own - the focus of it started out on making a workbench, but that has sort of “morphed” into creation of an actual Workshop - a good space to get things done physically and of merit.
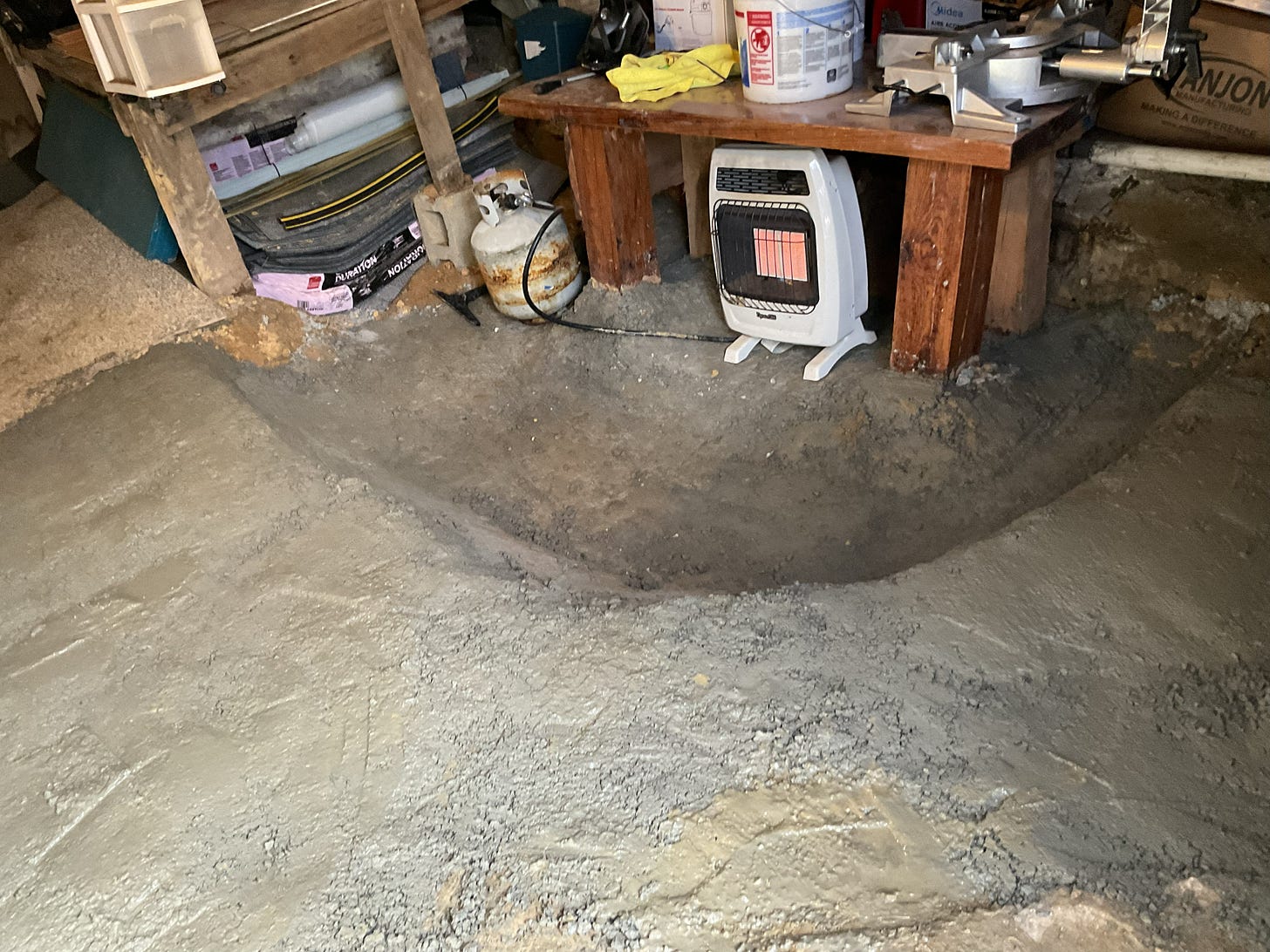
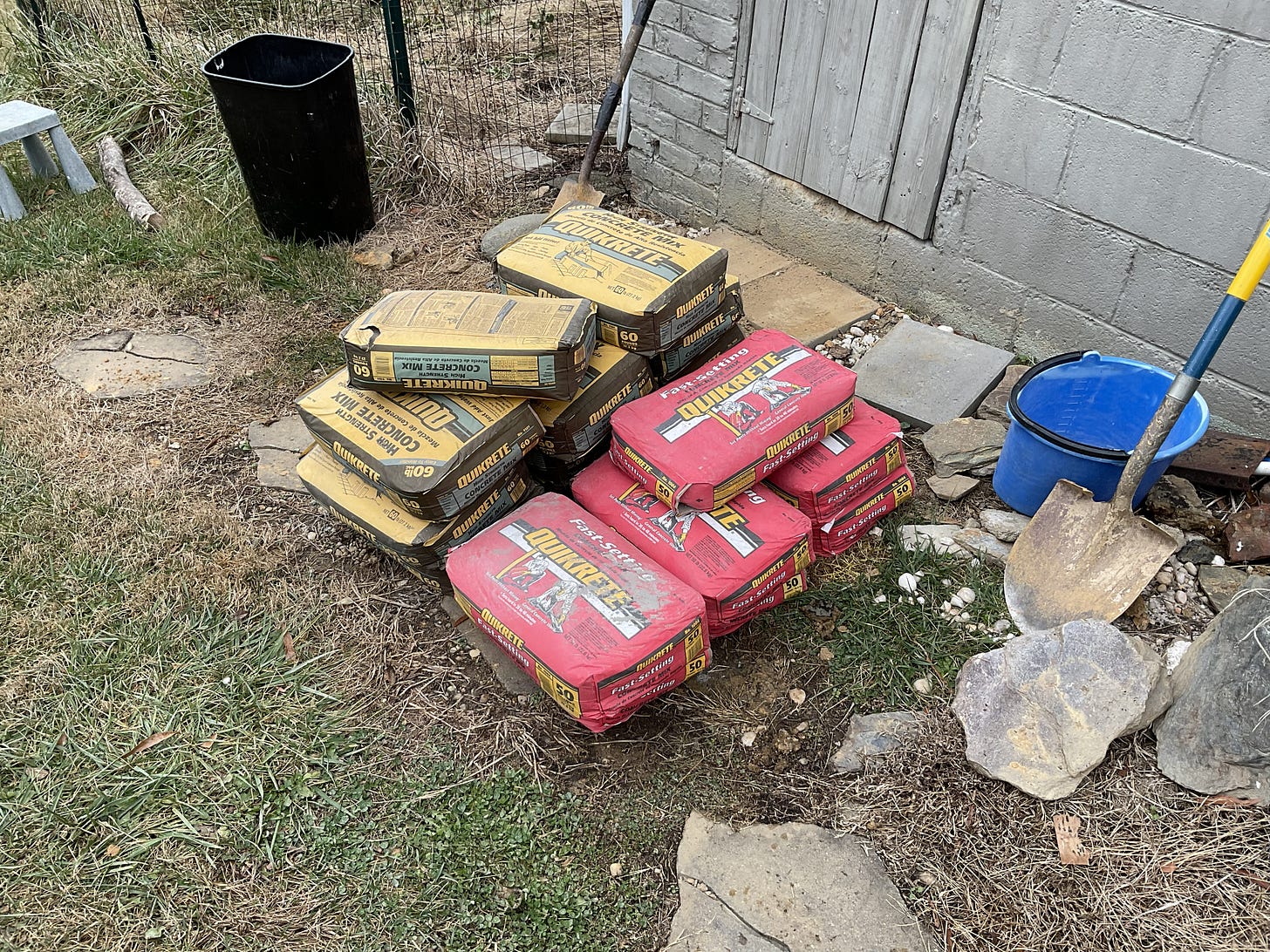
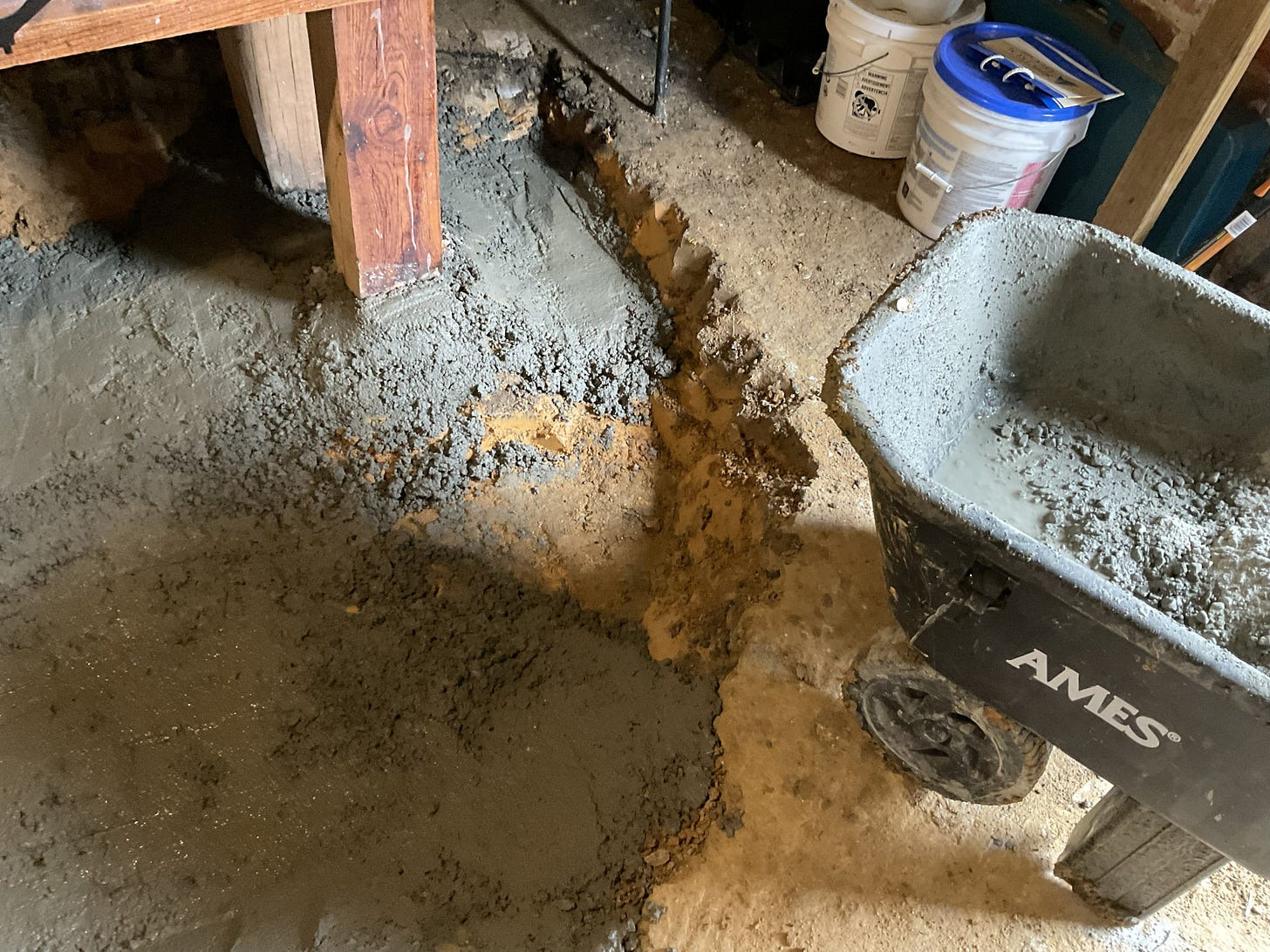
The focus below is on putting down some concrete - I wasn’t going for “perfection” cause I don’t have time for that and really beyond a certain level of thickness and smoothness there really are “diminishing returns” associated with the work effort and so I strive for balance in that regard cause like I said - I got a lot going on!
So - here is the latest:
It may not look “perty” but it will be functional and you would be surprised just how much dirt was dug out to get to this point and how many times I moved things around…..there is still more tidying up to do. If your curious about the sequence of this project - more details on that are in the article below:
~~ Here are a few more images ~~
~~~~~~
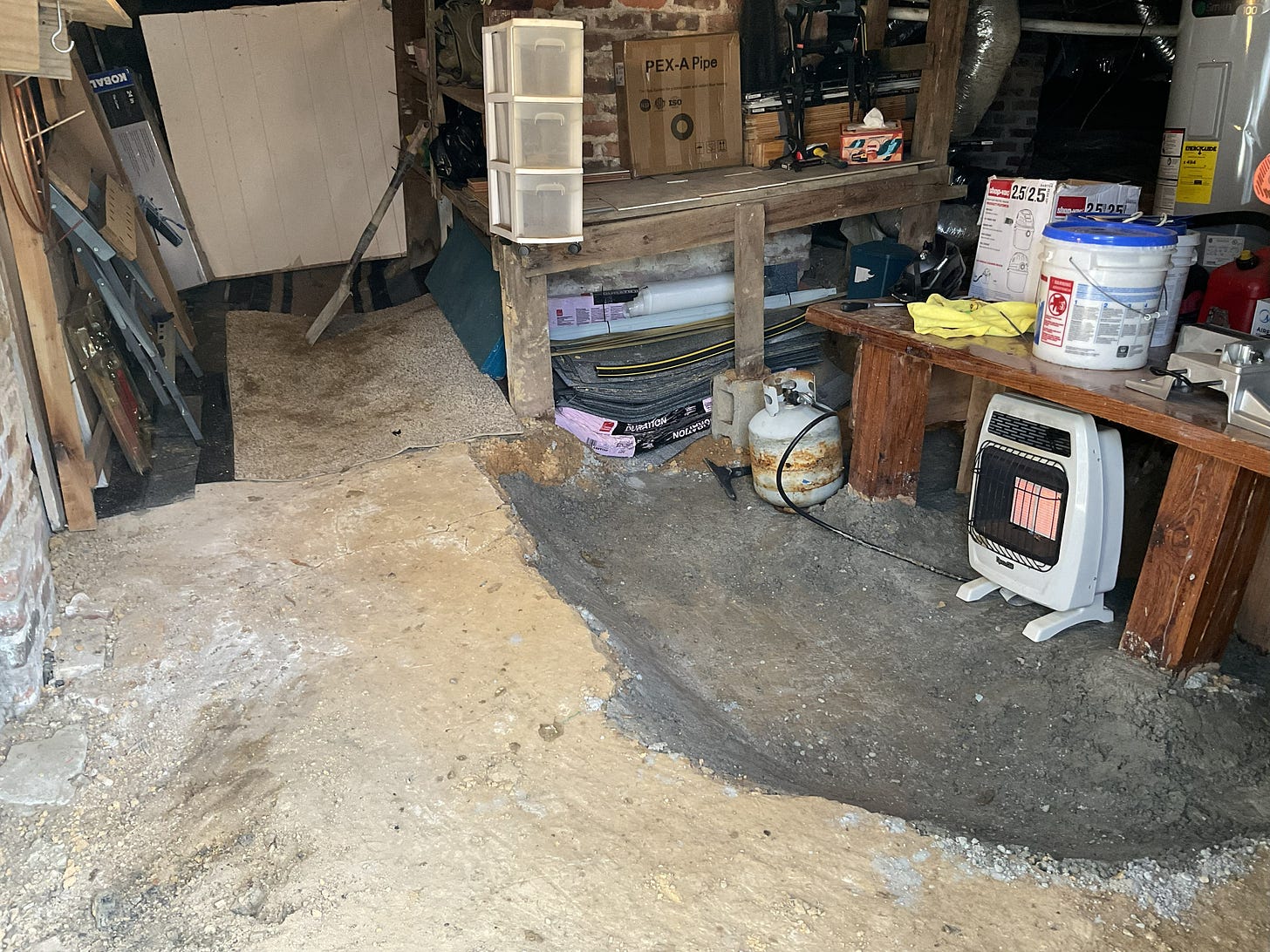
So now I think the dust in the workshop will be minimized - and I’ve created some good shelf-space and improved organization (some items had to be moved elsewhere).
I’ve got some workbench accessories on the way and will share an update after they are installed - and I think now I’ve got a decent workshop ready to support the next upcoming serious project which is going to be a solar panel installation with batteries that I intend on using - hopefully that gets done before the end of the year and I I’ll details on this so that others can do likewise if they so desire - I think it is going to be most worthwhile cause the price of panels and batteries has come down enough that this effort is much more feasible - so I’m going to do it. All the parts have either been delivered or are on order. Stay tuned for an article on that!
~~~
Lastly - I leave you with this:
Go Bills!
BK, 12625 1233
~~~
Porter on the way!
I ain’t kidding around - are you!
Don’t.
Porter on the way.
BK, 12625 1648
I show the final ingredient of the Porter - the yeast gets it fermenting - there is a lot going on at Green Garnet’s Potion shop - don’t come here with bad will or intent - if you do - forces are in place to defend.
Irish Ale Yeast will be what ferments this Boston Porter!
~
Don’t cause harm when porter is being brewed - come on - some of us have connections - way back to the beginning of the time the folks from the Old Land came to the New Land - and my kin - he was respectful - and so am I - and so ought you be - cause if you ain’t - then….well…No Boston Porter for you!
If you are - then - welcome to Green Garnets Shop - lots going on here - busy work and that is good - is it not?
BK, 12625 17174
Ps - the next update won’t be till the workbench accoutrements arrive.
~~~~
This is proof that I am alive!
Lay low Candace - really!
We got your back!
BK, 12625 1873
~~~~
Tis another nail-biter in Buffalo - I don’t think I’m gonna watch - but I Billieve no matter what in my hometown team!
Now - here is a teaser - I didn’t sleep well last night - I had solar panels on my mind - and I conducted some “tests” today - and now I have firmed the details of my plan!
Here is the teaser:
You know as a “retired” engineering professional it really gives me pleasure working with and trying to figure out - the best way to use these panels. But my plan has firmed and the next article will go into all the details - maybe more than the average reader would desire - but I’m telling you - I got a good plan!
Stay tuned!
BK, 12725 1552
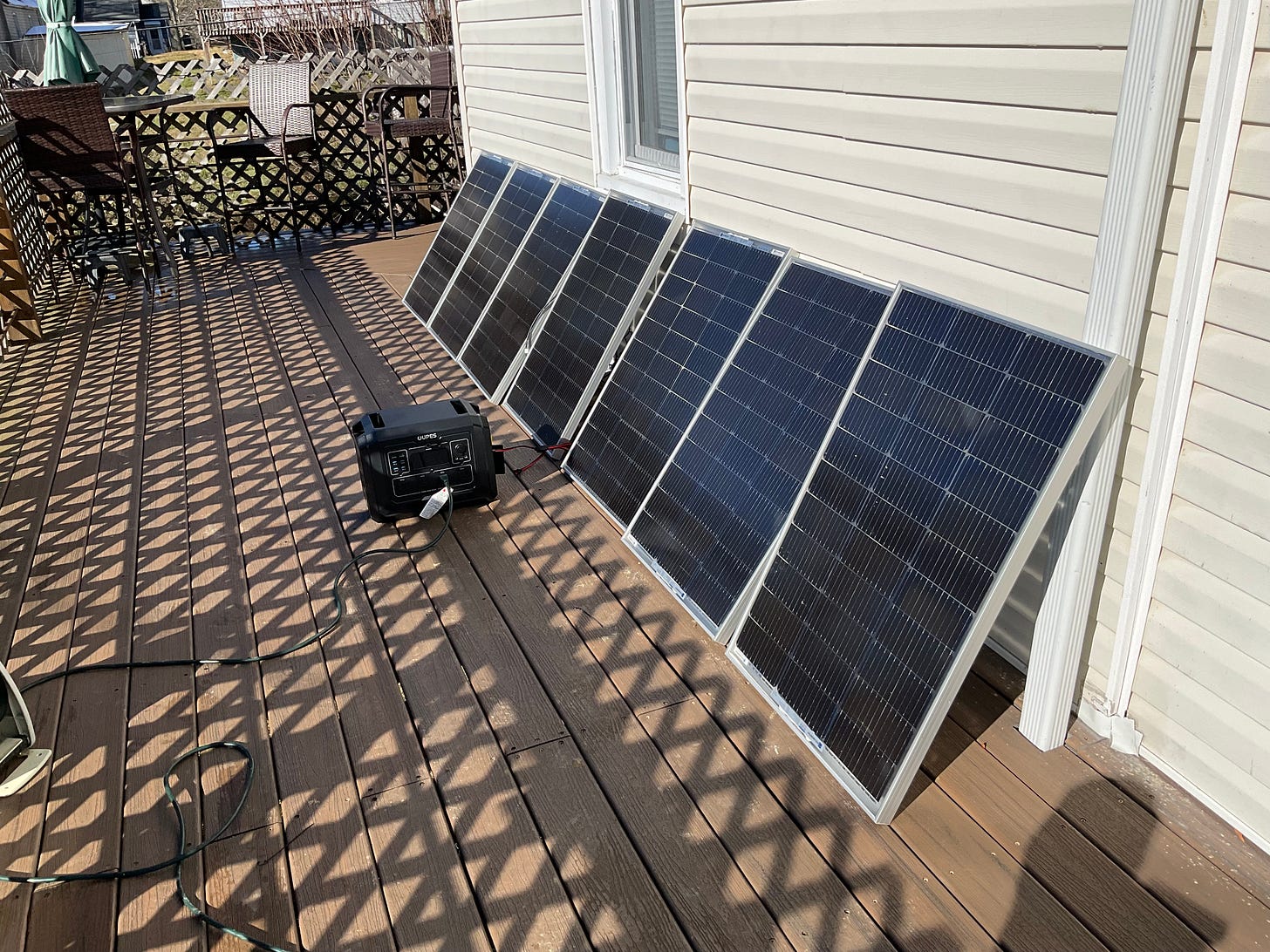












So I guess I'm like my daughter in a way - I can't keep a secret!
The panels are gonna be affixed to the siding of the home where the sun comes in - and then that will be that. I got 12 panels in total - four on order and now I know the wiring it takes to get this going and I ain't gonna wrestle with myself regarding orientation of the panels - cause they didn't cost much and it hardly is worth my life trying to install them somewhere difficult, so I know where they are gonna be affixed and then that is that. They will power the batteries on order but yet to be delivered - and then consider that self-sufficient insurance policy!
Seriously - some of us plan in advance - and Central Power is so 20th century thinking!
May the best ideas prevail I say - I ain't kidding around.
I would like to put in a "thanks" to the Brave-AI - (see previous articles) - regarding its feedback on the concept of "distributed generation". And this is "on-topic" in the post above being I gonna setup a small-scale solar powered setup next week - so read this if you are interested - from the ai direct:
~~
Decentralized power, also known as distributed generation or decentralized energy, refers to the generation of electricity at or near the location where it is consumed, rather than relying on large, centralized power plants.
This approach involves small-scale power generation units such as solar panels, wind turbines, biomass systems, small hydroelectric plants, and combined heat and power (CHP) systems, which are interconnected within local energy distribution networks.
These systems, collectively known as distributed energy resources (DERs), are typically located close to the load they serve and have capacities of 10 megawatts (MW) or less.
The shift toward decentralized power is driven by several factors, including the rising demand for sustainable and reliable energy, the need to reduce dependence on centralized grids, and the push to combat climate change through clean energy technologies.
By generating power locally, decentralized systems reduce transmission and distribution losses—estimated at about 5% in the United States—thereby improving overall grid efficiency.
They also enhance grid resilience, especially when integrated into microgrids, which can operate autonomously during grid outages.
Technological advancements such as smart meters, internet connectivity, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning are essential for managing decentralized systems, enabling real-time data exchange, demand forecasting, and dynamic load balancing.
Smart contracts and blockchain technology are also being explored to facilitate peer-to-peer energy trading, as seen in projects like the Brooklyn Microgrid, where solar energy producers can sell excess power directly to neighbors.
Virtual power plants (VPPs) aggregate multiple DERs into a single, manageable resource, enhancing grid stability and efficiency.
Despite its benefits, decentralization presents challenges. The intermittent nature of renewable sources like solar and wind requires backup generation or large-scale energy storage to ensure reliability.
Cybersecurity risks are heightened due to the increased number of connected devices and potential vulnerabilities in control systems, as demonstrated by incidents involving solar inverters being remotely disabled.
Additionally, not all power grids are equipped for two-way power flows, smart metering, or reliable internet connectivity, which are necessary for effective decentralized management.
Regulatory and policy reforms are evolving to support this transition. For example, the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act provides investment tax credits to stimulate grid-scale battery storage, while the EU’s NIS2 directive strengthens cybersecurity requirements for energy infrastructure.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) projects that over 100 million households could have rooftop solar panels by 2030, reflecting the accelerating pace of decentralization.
As the global decentralized power generation market grows, it is expected to play a pivotal role in achieving net-zero emissions and building a more resilient, efficient, and democratized energy future.
~~ cut & paste with no edits ~~
BK, 12625 1407